How to choose between conventional safety relief valve and pilot operated safety relief valves
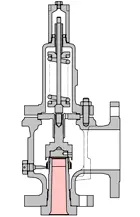
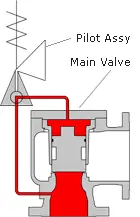
(L) Conventional Safety Valve and (R) Pilot Operated Safety Valve
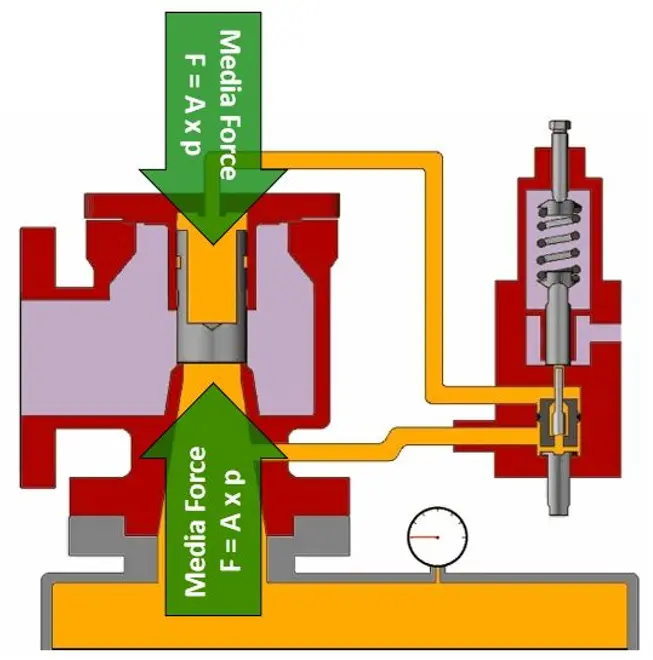
Because of the difference in area and pressure being equal, the force on the top of the piston is higher than the force on the piston at the nozzle. Because of that, as liquid pressure increases, the sealing force of the piston increases at the same time. When set pressure is reached, the pilot valve relieves the pressurized fluid from the dome area atop the piston, allowing process pressure at the nozzle to force the piston upward from its seat, which allows the valve to open and relieve pressure in the pipeline.
Conventional spring-operated safety valve is most likely to be the best for the applications that will expose the valve to high temperatures, highly viscous, or dirty services. In smaller sizes they are greatly cheaper to use than POSVs, and most designs will follow standard API 526 center-to-face flange dimensions.
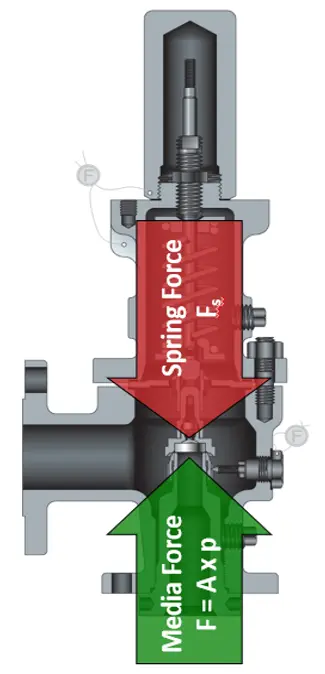
Conventional spring-loaded safety valve may not be the good choice for applications requiring maximum seat tightness / sealing, minimal simmer, or applications with high or variable back pressures. Measures can be taken to mitigate these shortcomings; however they bring limitations of their own. For example, a conventional valve can be constructed with a soft seat to improve sealing, but this will generally introduce temperature limitations. To reduce the effects of back pressure a conventional PRV can be outfitted with a bellows. However, a bellows has lower back pressure tolerance than a POSV and can be more costly to maintain.
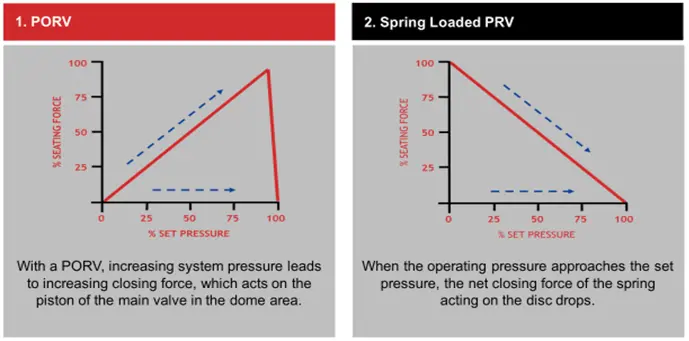
Comparison of closing forces: POSV vs Spring Loaded (Conventional) PRV
The POSV is designed to mitigate many shortcomings of a conventional valve but has its own limitations. POSVs are best suited to applications requiring maximum seat tightness when approaching set pressure, applications with superimposed back pressure and built-up back pressure, and high relieving capacity applications with physical size limitations, to name a few. POSVs can also have set pressure capabilities that go beyond API 526 set pressure limitations associated with conventional PRVs.
Next: API6D Valve types
Previous: Types of Safety Valve | Shinjo China