HOW DO YOU MAKE USE OF THE INFO ON A PUMP CURVE TO PICK A PUMP IN MY SYSTEM?
These curves contain very important data that pump users have to evaluate and interpret for correct pump selection and efficient operation.
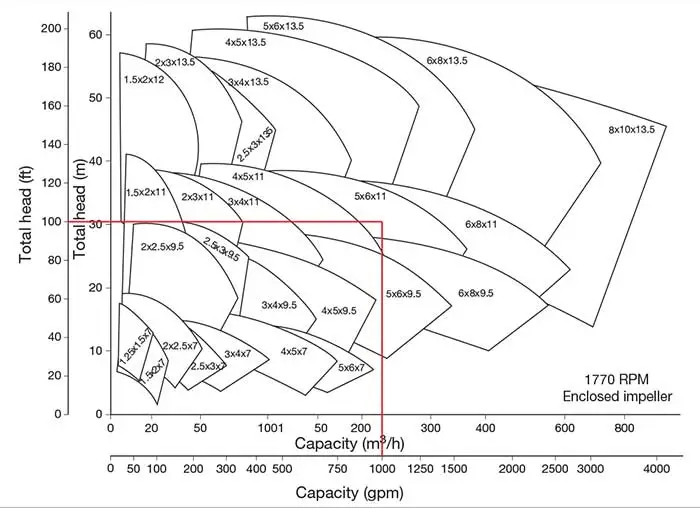
Image 1. Pump family selection chartImage 1. Pump family selection chart (Images thanks to HI)
You will find three primary kinds of pump curves provided by the pump manufacturer: the choice chart has proven in Image 1, the printed curve proven in Image 2, the certified curve
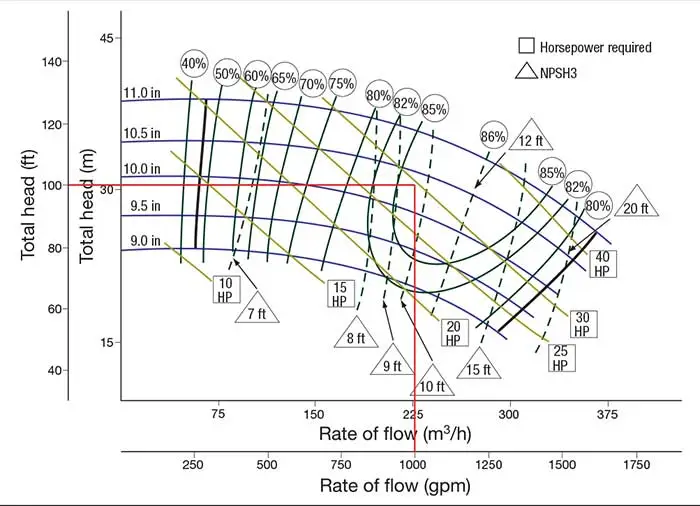
Image 2. Printed pump curveImage 2. Printed pump curve
The certified curve differs from the choice chart and printed curve since it is for that specific pump and impeller trim purchased and never the overall products. Frequently it'll range from the acceptance test standard and acceptance grade the pump was tested against.
ADVERTISEMENT
The choice chart shows the different pump sizes readily available for confirmed manufacturer's pump line and speed. The preferred mind and flow minute rates are joined around the curve, and also the pumps that overlap the region are valid options to consider for selection. The choice chart is helpful in creating a narrow your search of pumps for consideration. For instance, when the application known as for any pump running in a nominal 1,800 revolutions each minute (revolutions per minute), that may provide 1,000 gallons each minute (GPM) at 100 ft of total mind, the chart implies that 5 × 6 × 11 and 6 × 8 × 11 size pumps overlap around the selection chart and will probably be the 2 best sizes to judge further.
Even though the printed curve may appear confusing, lots of information could be obtained from this pump curve. Should you comprehend the charts, you'll take advantage of the data they provide. Remember:
The Y-axis (Vertical Multistage Centrifugal Pump) about this curve may be the mind in ft and meters, and also the X-axis (horizontal) may be the capacity (flow rate) in m3/h and GPM.
Each downward sloping blue lines are known as a mental capacity curve.
Each number over the mind capacity curves right from the Y-axis represent different impeller diameters. The total mind is reduced once the impeller diameter is reduced.
The figures within the circles over the topmost mind capacity curve would be the pump efficiency, and also the lines stemming from all of these circles are lines of constant efficiency. The triangles which contain several and word “NPSH” are constant lines of NPSH (in ft) the system must supply for that pump to function having a 3 % mind loss. NPSH margin above this value is needed for that pump to function in the printed mind.
The diagonal lines running with the mental capacity curves signify lines of constant pump input power.
While using selection chart to narrow lower the right pump's size for that duty reason for 1,000 GPM and 100 ft of mind, the manufacturer's printed curves could be referenced to assist determine the very best pump to have an application. Image 1 shows the printed curve for any 5 × 6 × 11 pumps running at 1,770 revolutions per minute. Information could be produced from the manufacturer's pump curve with this application, such as the following:
The impeller diameter that fits the job point falls between 10 and 10.5 inches.
The pump is 85 % efficient at the rated point and 86 percent efficient in the best efficiency point (BEP).
In the rated point, the shaft power is going to be between 25 horsepower (hp) and 30 hp. To make sure a non-overloading condition in the finish from the curve, a 40-hp motor might be needed.
NPSH3 is between 9 and 10 ft in the duty point.
Observe that data shown on a manufacturer's pump curve is dependant on 68°F or 20°C water. If your liquid apart from water is going to be pumped, info on the manufacturer's printed curve should be adjusted for that liquid density and viscosity, which affects the mind, flow, efficiency and pump input power.